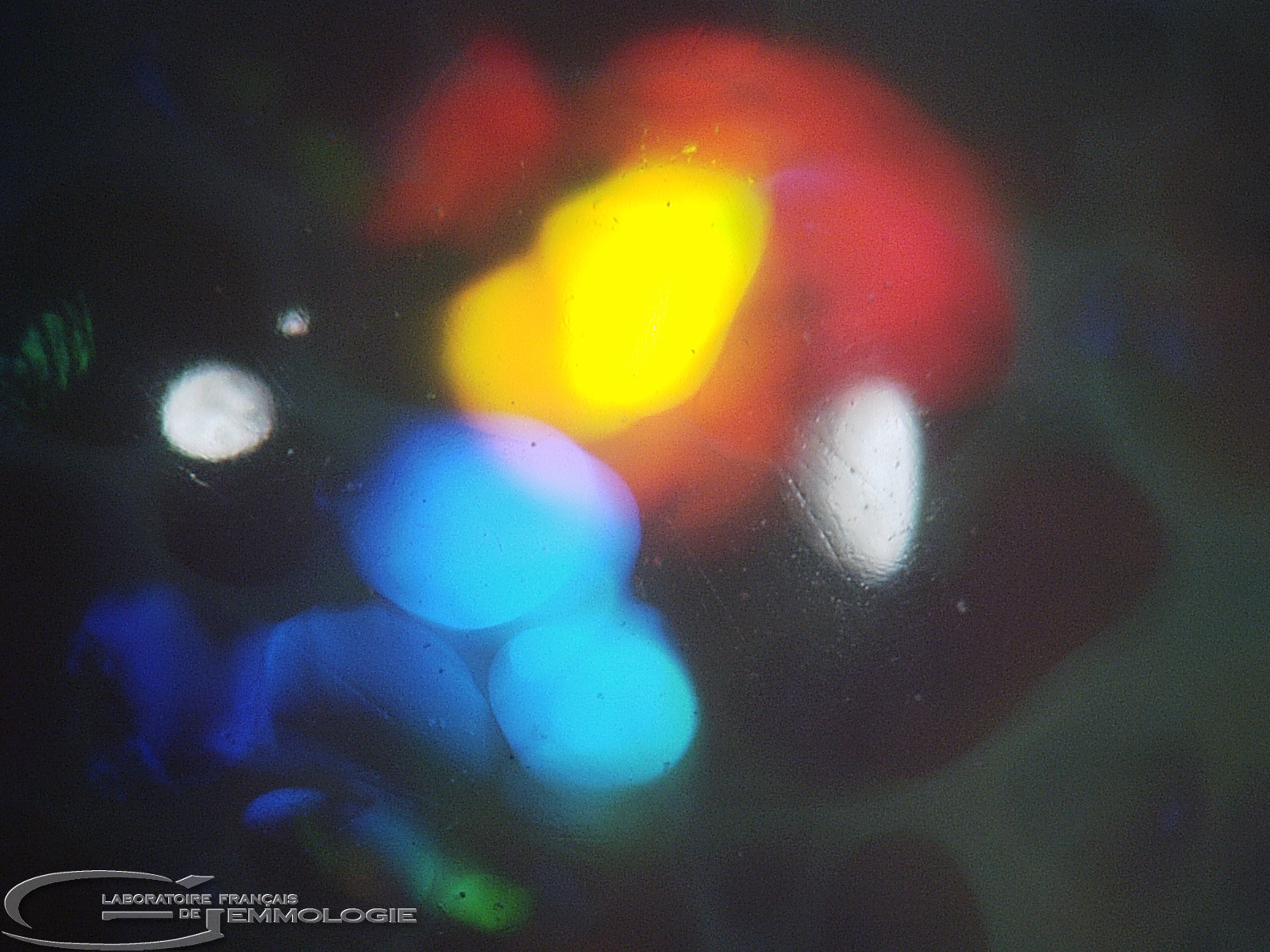GEMSTONE LIBRARY
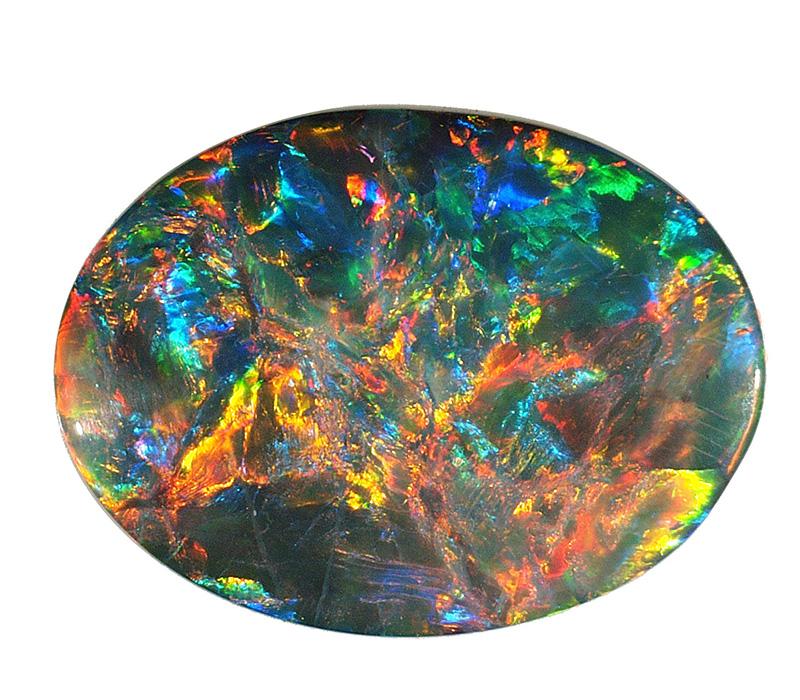
OPALS
Opals are hydrated silica. They can occur in a very wide variety of mass colours: black, grey, white, brown, orange, yellow, green, blue, etc. The opals can be divided into two groups: common opals without colour effects, and noble opals with colour effects.
Noble opals can come mainly from Australia, Ethiopia or Brazil. As to fire opals (orange in colour), they come from Mexico, Ethiopia or Madagascar.
Noble opals are written up in a different analysis report from LFG. The mass colour is graded and the colour effects are described to show each stone at its best.
CHARACTERISTICS
- Name: Opal
- Mineralogical nature: Opal
- Colour: Colour in mass: colourless, white, yellow, orange (fire opal), red, brown, black, grey, pink, green, blue, violet
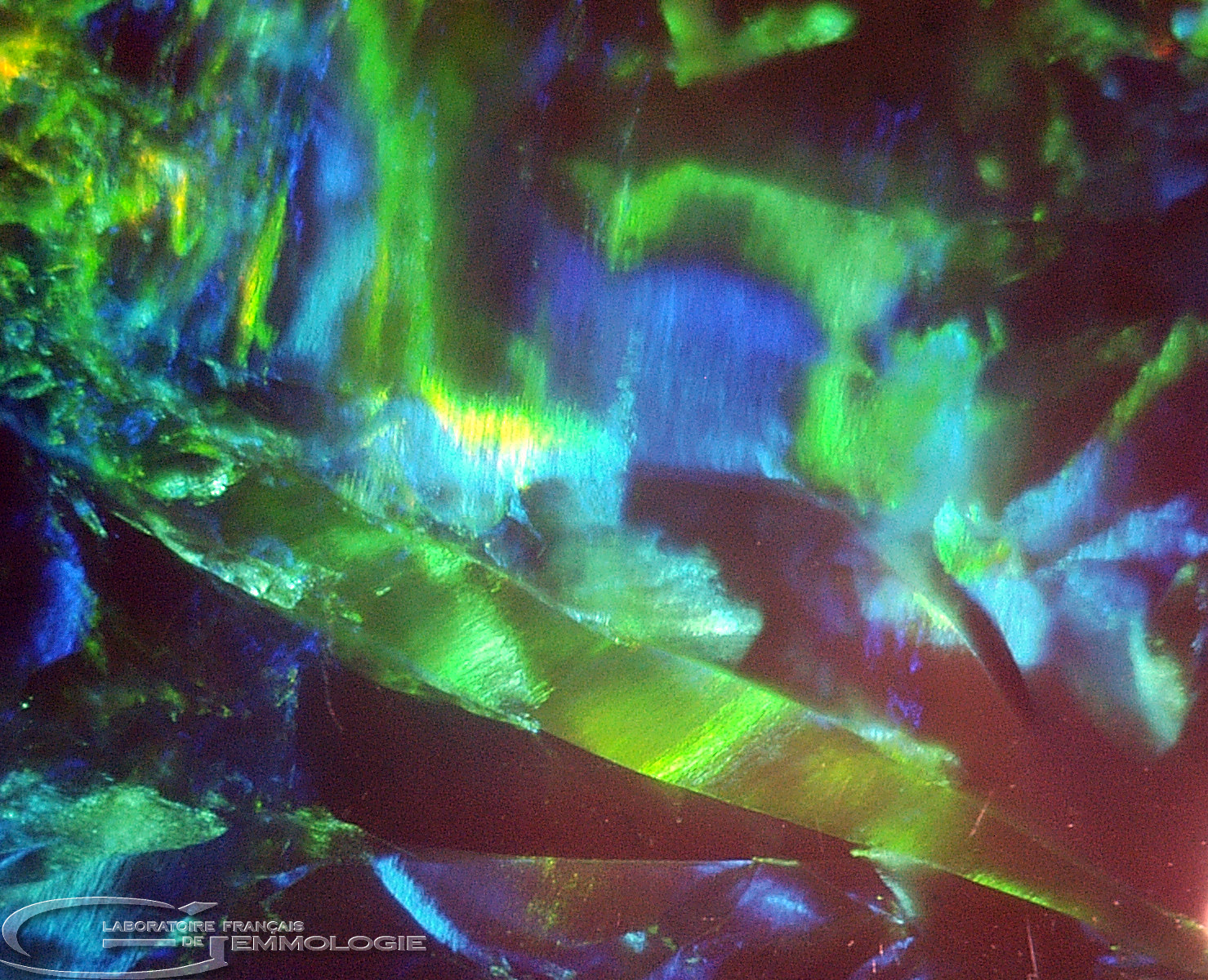
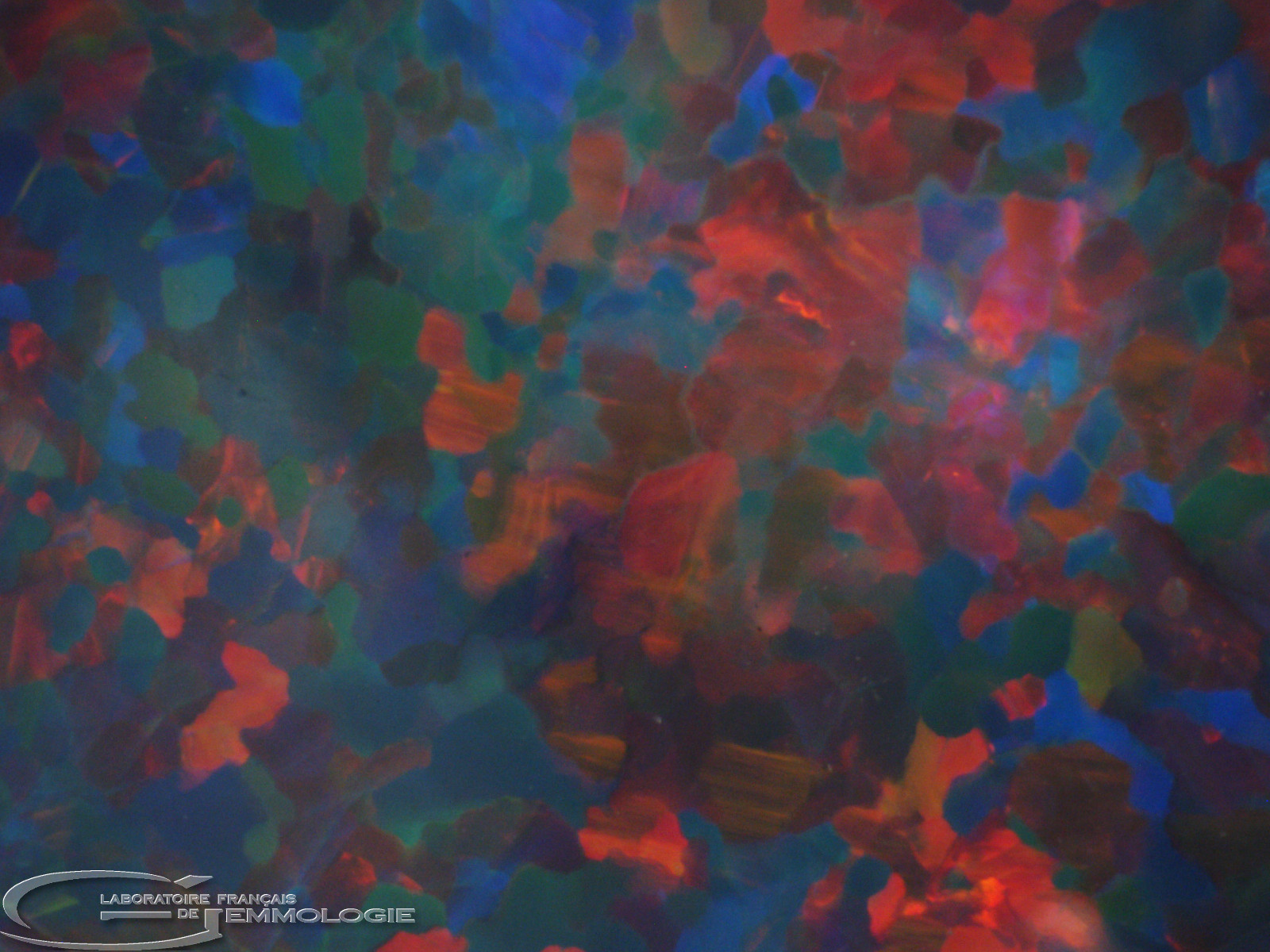
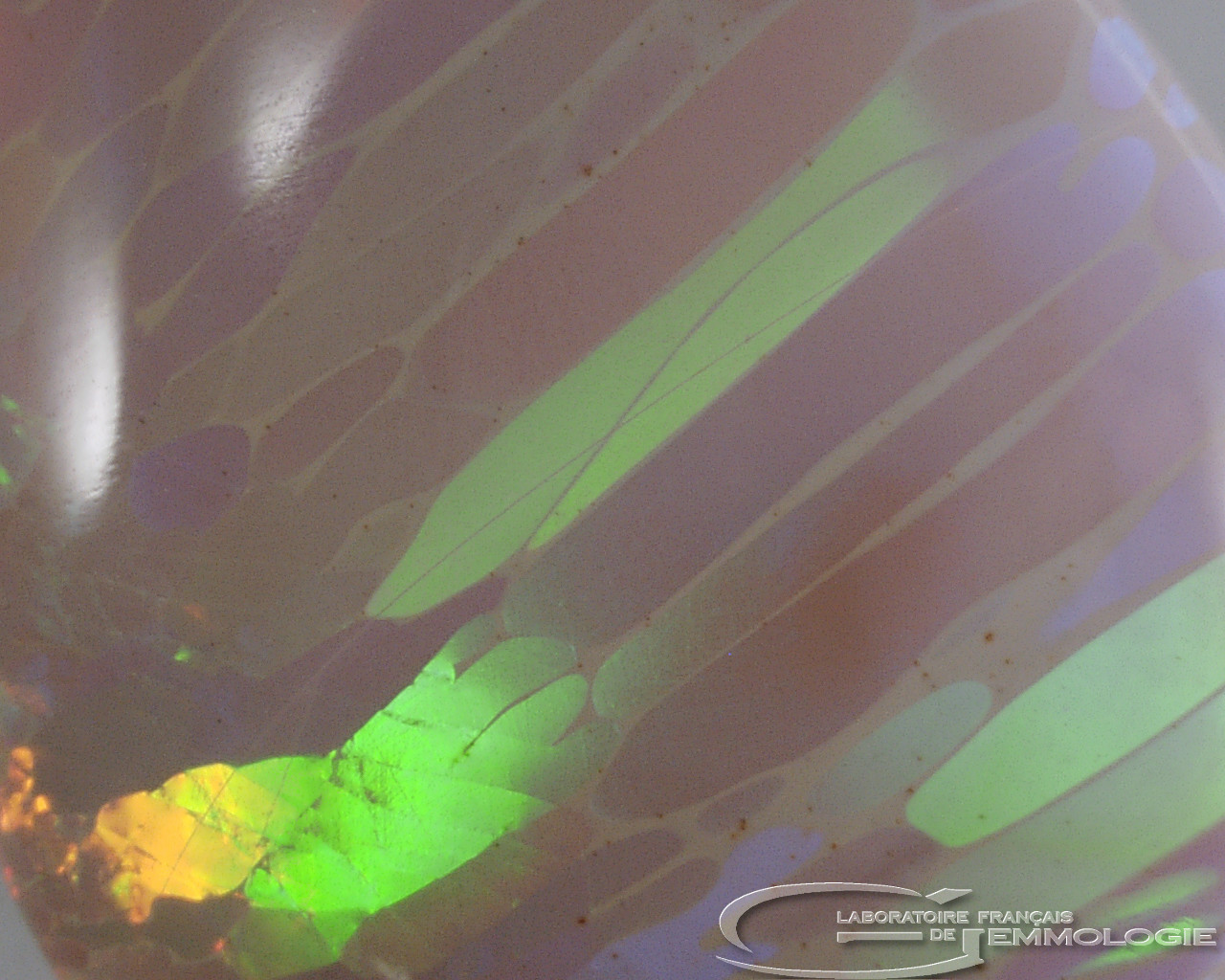
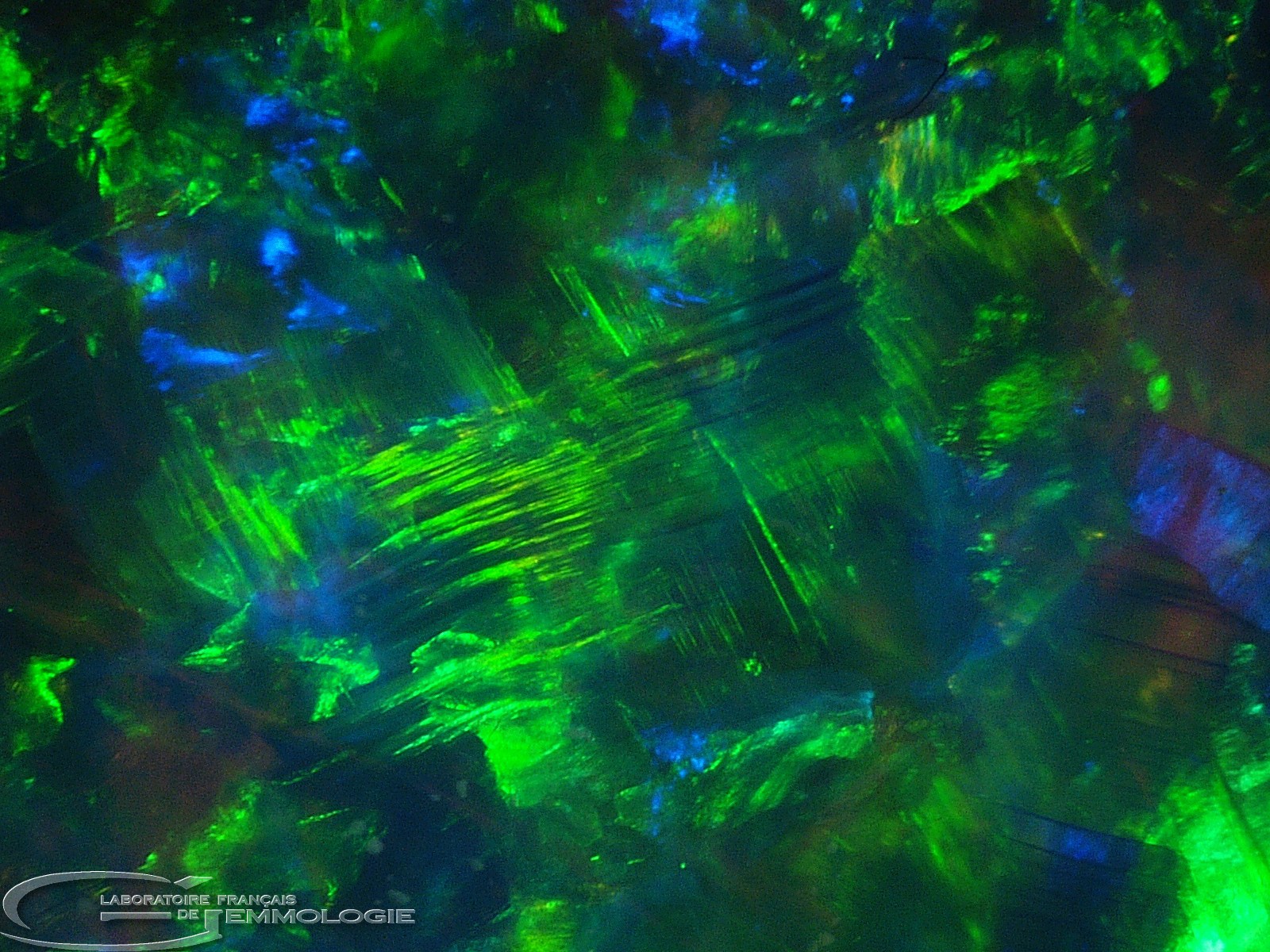
- Diffraction colours: all the colours in the spectrum
- Crystal system: Amorphous
- Chemical composition: SiO2, nH2O
- Causes of colour: Diffraction where noble opals are concerned (with colour effects), submicroscopic inclusions of various minerals (chrysocolla, arsenic sulphide, hematite, cinnabar, etc.)
- Density: 1.90 to 02:20
- Hardness: 5,5 to 6
- Cleavage: None
- Fracture: Conchoidal
- Optic sign: Isotropic
- Refractive index: 1.420 to 1.460
- Birefringence: Null
- Dispersion: Low
- Pleochroism: Null
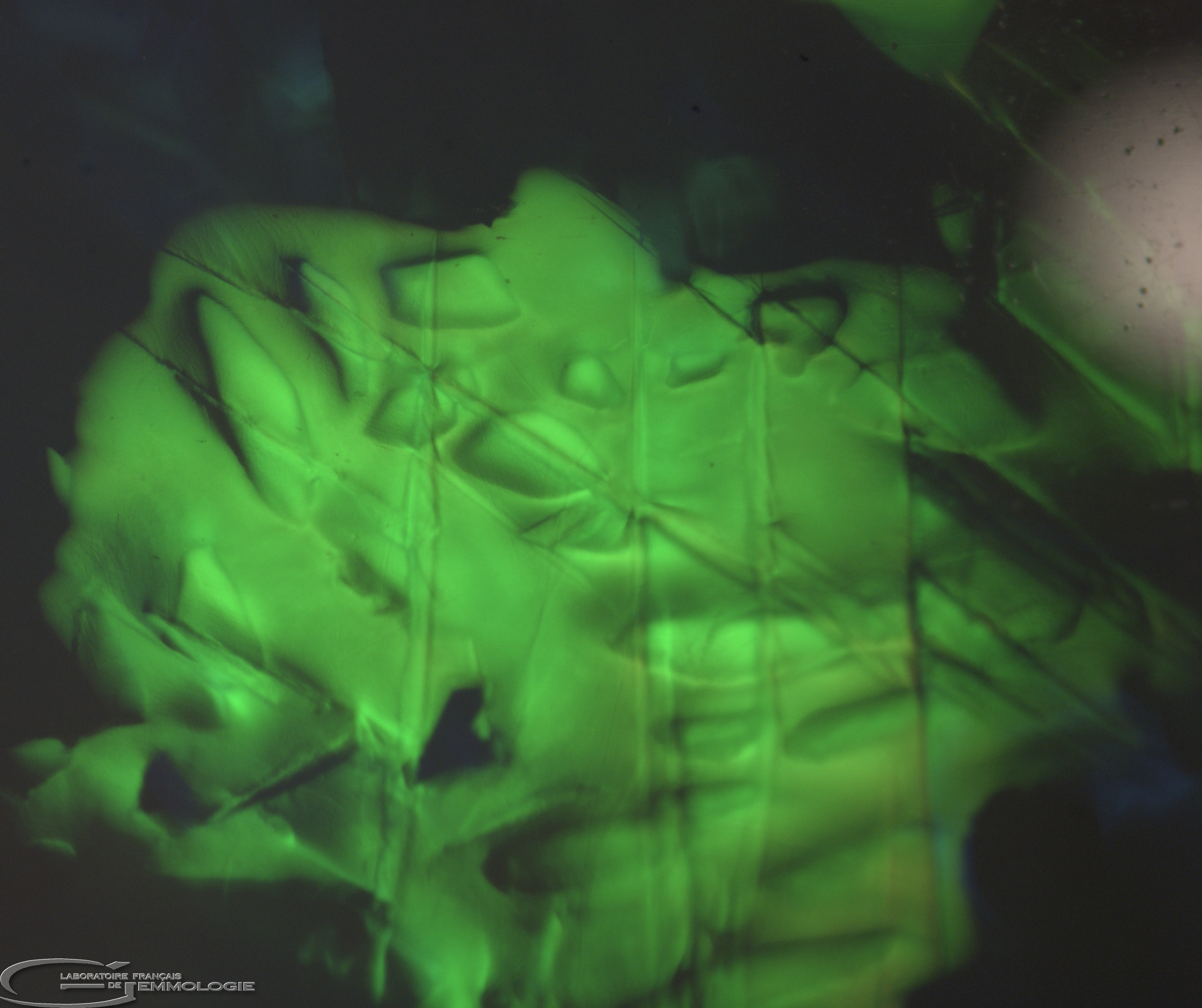
- UVL: Inert to blue, white, yellow to green
- UVC: Idem
- Treatments: Dyeing
- Syntheses: Anhydrous syntheses
- Syntheses with polymers